
Sustainability for Flexible Packaging – Our Views
What is Sustainability?
Sustainability calls for us to maintain a balance between environmental, social equity and economic needs. To promote the concept of looking at things in a holistic manner, sustainability is associated with blue colour, the colour of our planet.
Benefits of Flexible Packaging
Flexible packaging is often the target of environmentalists due to concerns with its end-of-life use. However, one must not ignore that flexible packaging is by far the most efficient form of packaging for most categories due to its light weight and ability to increase the life of the material packed. Light-weighting ensures that the least amount of energy is used in packaging and shipping of a product and at the same time the least amount of waste is generated after-use. Any alternative material with a lower carbon footprint, must not result in a reduction in the shelf-life of the products packaged in it else the losses would be far greater than the benefits achieved by changing the packaging material.
What happens to Flexible Packaging waste post-use?
Most often, flexible packaging waste ends up either in dump yards or landfill sites. In lesser developed countries, since this form of waste does not carry any economic value, there is no incentive for the rag-pickers to collect this material and hence it adds to the street litter which has a negative impact through pollution of water bodies & underground water, blockage of drainage systems, leaching and causing animal deaths by ingestion.
Our views on Flexible Packaging waste
In our perspective, if we are able to improve upon the end-of-life solutions for flexible packaging materials, we would have a truly sustainable medium for bringing food and other products from the producers to the hands of the consumers. This can come about through the development of technologies which are able to handle highly contaminated, light weight mixed plastic waste. This has to be coupled with initiatives to provide an economic incentive for the collection of such waste, which can only be sustained through Extended Producer Responsibility.
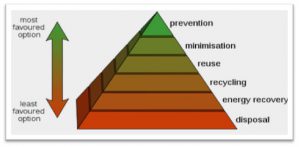
The existing technologies are mostly focusing upon waste-to-energy or plastics-to-fuel. The environmental impact of these and the overall effectiveness is subject to debate.
Eco Blue’s endeavour is to commercially develop technologies which help reduce the negative impact of flexible packaging waste.
Our views on Bio-Plastics and Biodegradable Plastics
A lot of resources have also been deployed in the development of biodegradable films for flexible packaging. EcoBlue does not endorse these products in their current form for use in laminates. Their biodegradability is subject to environment conditions which in most cases are not available. Bio-plastics, or plastics made from an organic source, compete with farming resources which could be used in growing food products, that may or may not be biodegradable in nature.
